Introduction
Zara is a Spanish company that retails in clothing and accessories. Zara specializes in fast fashion, and products constituting clothing, accessories, shoes, swimwear, beauty, and perfumes. The Business Plan of Zara includes perfectly structured, and there isn’t a single business operation that is solely responsible for the success of this brand.
It is the largest company in the Inditex group with Bershka, the world’s largest apparel retailer. Zara as of 2020 manages more than 20 clothing collections a year.
Amancio Ortega and Rosalia Mera are the founders of Zara. The biggest Zara store is in Madrid, Spain.
Key Resources
The key resources of Zara are:
- Experienced store managers
- RFID technology
- Supply chain excellence
- Effective production and logistics process
- Using high-tech software

There are 2007 Zara stores in 96 countries.
The Business model of Zara consists of vertical integration and logistics trade-offs. These two strategies play a significant role in the success and global recognition that Zara receives. Vertical integrations help the company to control all of its verticals like design, manufacture, shipment, distribution, etc.
In spite of being a fast-fashion brand, it holds a position of superiority over its contemporaries due to the efficiency of the business model of Zara. This unparalleled and unprecedented business model is one of the primary reasons for the success rate of Zara.
Revenue Model of Zara
The Spanish fast-fashion store Zara generated online net sales of around US$2 billion in 2018. For 2019, revenue of up to US$2.5 billion is projected. Zara revenue generation is based upon its selling of more than 450 million products per year, i.e, it works on economy of scale. Zara has 1700 stores in more than 86 countries around the world
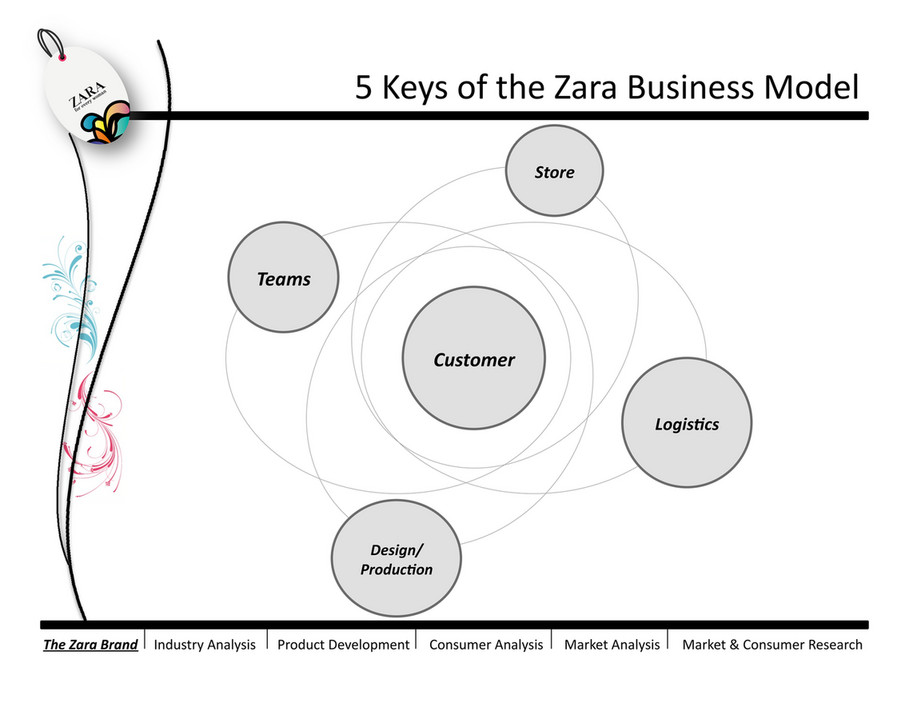
Zara Business Model
In recent years, the concept of fast fashion has emerged as an important trend. Fast fashion ensures that the clothes being manufactured follow the ongoing trends and follow the customer’s demands. Zara is a Spanish company that retails in clothing and accessories. Zara specializes in fast fashion, and products constituting clothing, accessories, shoes, swimwear, beauty, and perfumes.
Revenue Model of Zara
The Spanish fast-fashion store Zara generated online net sales of around US$2 billion in 2018. For 2019, revenue of up to US$2.5 billion is projected. Zara revenue generation is based upon its selling of more than 450 million products per year, i.e, it works on economy of scale. Zara has 1700 stores in more than 86 countries around the world.
Total sales of the company are around the US $13 billion that makes it one of the top 3 largest fast fashion brands in the world. Key strategies that help the company generate good revenues are-
- In-time production and distribution- Makes are the production and distribution are at the right time.
- Trendsetter- becoming a trendsetter at the right time
- Effective distribution management- by reducing the delivery time
- No costs on the advertising and marketing
Early History
Founded by Amancio Ortega in 1975, Zara is a flagship clothing chain store that is part of Inditex group, the world’s largest apparel retailer. Amancio Ortega opened the first Zara store in 1975 in central A Coruña, Galicia, Spain where the company is still based. Ortega initially named the store Zorba after the classic 1964 film Zorba the Greek, but after learning there was a bar with the same name two blocks away, the letters were remolded for the sign to say “Zara”. It is believed the extra a came from an additional set of letters that had been made for the company. The first store featured low-priced lookalike products of popular, higher-end clothing fashions. Ortega opened additional stores throughout Spain. During the 1980s, Ortega changed the design, manufacturing, and distribution process to reduce lead times and react to new trends in a quicker way, which he called “instant fashions”. The improvements included the use of information technology and groups of designers instead of individuals.
SWOT Analysis
Zara is mainly based on a concept called fast fashion. It is similar to the idea of FMCG i.e., Fast moving Consumer Goods. Fast fashion is used to target an audience which majorly comprises young adults and middle-aged people. The cycle of fast fashion ends early as the fabric of the cloth withers. Various brands like Forever 21, H&M have incorporated this idea into their business model.

Strengths in the SWOT Analysis of Zara
- Spacious stores: Zara have more than 2000 stores all over the world. Part of one of the most biggest Spanish retailers in the world
2. Global reach: Zara have a well established brand name worldwide
3. Their supply chain management is extremely low cost as well as most of their processes like operations, manufacturing are all vertically integrated
4. Brand valuation: Strong online presence through their own website and other ecommerce platforms makes Zara a popular brand name
5. Affordable prices: Clothes are produced at a competitive price with the most innovative and fashionable designs.
6. Fashionable clothing: Zara offers extremely trendy, well designed and fast delivery of new products. Apart from clothes, Zara also offers handbags, shows etc.
Weaknesses in the SWOT Analysis of Zara
- Limited advertising: Limited marketing and advertising as compared to some other brands
2. High competition for Zara means limited market share and high brand switching
3. Zara is perceived to be an expensive brand
4. Insufficient product information: Zara is not very active in the online space though it is available through online channels with partners.
Opportunities in the SWOT Analysis of Zara
- Wide global market: There are more global markets which Zara can explore.
2. They can also enter into segments and expand those areas where they haven’t.
3. Online channels: Online marketing and ecommerce is gaining importance which can be tapped by Zara.
Threats in the SWOT Analysis of Zara
- Fast fashion competition: The high end fashion merchandisers can be a major threat to them. There is a large amount of consumer switching taking place
2. COVID-19 pandemic: Economic downturn can also be a threat to their target segment
3. Imitations: Fake imitations can decline the sale of Zara products and hurt business
Conclusion
Zara prides itself on remaining on top of the latest trends and radiating an upscale vibe, but its production process is the real show-stealer. These industry-leading procedures elevate it from a mere clothing store to a market leader in fast fashion executed well. Zara excels at guaranteeing that everything goes as planned, as it has more control over its production and business network than most of its competitors.




